Addressing Supply Chain Finance Cyber Security Risks
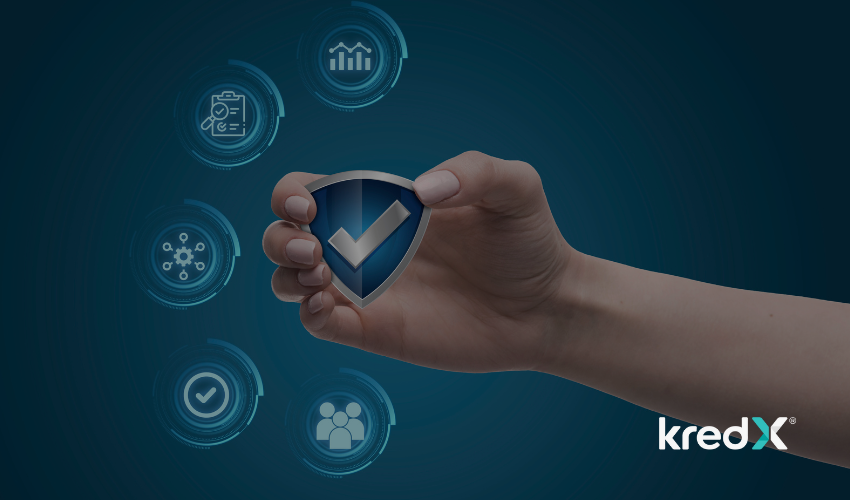
Supply chain attacks are designed to exploit trust relationships between an organization and external parties. As supply chain finance is a form of financing received mostly in relation to open account trade to help both buyers and sellers maximize their working capital by lowering the risk of disruption in the supply chain.
Supply chain finance covers a range of working capital financing products that need to be secured from unknown cyber threats. Building these products to fulfill digital infrastructure and data connectivity, inlining with global standards and cyber security principles are the key objectives. While preserving the data identity and privacy, the data model framework allows interoperability between digital platforms for the seamless exchange of information and documents.
So at KredX, we help businesses by extending immediate access to cash flow solutions online, where our supply chain finance is a funding option available to both buyers and suppliers to help them even out working capital related complications, there are certain expectations about the ways information and assets to be managed and protected from both buyers and suppliers point of view, so we first establish and clearly communicate minimum security requirements to adhere.
Working with suppliers can deliver various benefits in trade finance such as reducing costs, increasing efficiencies and strengthening operations. As a result, modern supply chains often involve new cyber, human and machine error risks as well as thousands of third parties risks to companies’ systems and networks. These integrations enable suppliers to access the data they need to carry out their roles, but they can also increase organizations’ cyber risk by widening their potential attack surfaces.
Attackers hunt for insecure network protocols, unprotected or un-dedicated server infrastructures, and unsafe coding practices. As well as potential vulnerabilities in networked physical security devices, for example, a poorly secured access control or business surveillance system. They break in, change source codes, and hide malware in build and update processes. In such cases, using secure browsing tools like a top VPN download can be an added layer of defense to protect sensitive business information from prying eyes, especially when accessing platforms remotely.
To prevent these supply chain attacks, KredX deployed detection and response solutions that automatically detect and remediate suspicious activities and strong code integrity policies to allow only authorized users. It has also developed an intense incident response process for supply chain attacks so that timely notification is sent to customers with accurate information. Threat actors could exploit supply chains in various ways, so applying a risk-based approach requires understanding the assets critical for goals and objectives, where those assets are located across their people, process and technology, and the risks to the business if they were compromised.
For example, any potential contractual failures by continually monitoring key suppliers and the level of access they have to network applications; so by doing this, identification of unusual behaviour that could indicate an attack on the supply chain, such as misconfiguration of access credentials. Ultimately, a risk-based approach to supplier management forces us to pay attention to the data involved in supplier contracts and services.
Overall, a well defined system and processes while sharing trade finance documents among participants on a real time basis is on a “need-to-know” basis for the protection of data privacy and security. Further, it is also extremely important to analyze the data and infosec policies and regulations to follow.
Supply chain attacks are likely to be an increasingly common fact of life for businesses in the future. The threat of software supply chain attacks will also continue to grow. The best way to protect against the growing threat of supply chain attacks is to prepare today by devising cybersecurity procedures and establishing incident response plans that enable you to act quickly if a supply chain attack were to impact your business. As well as potential vulnerabilities in networked physical security devices, for example, a poorly secured access control or business surveillance system.